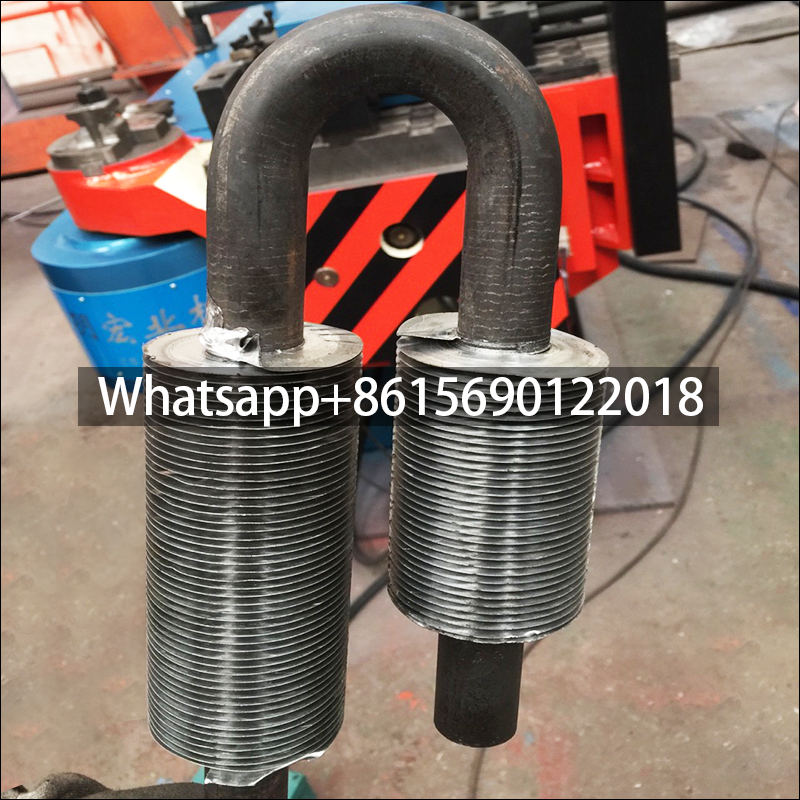
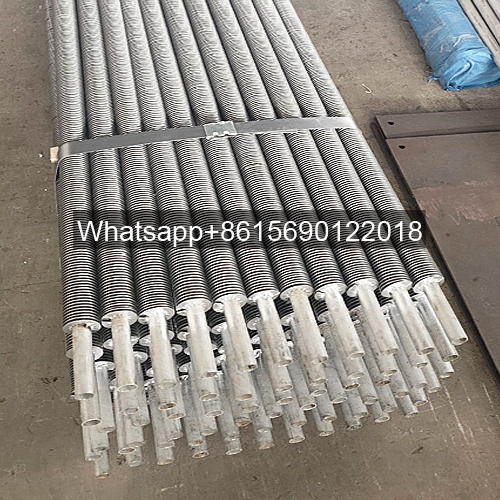
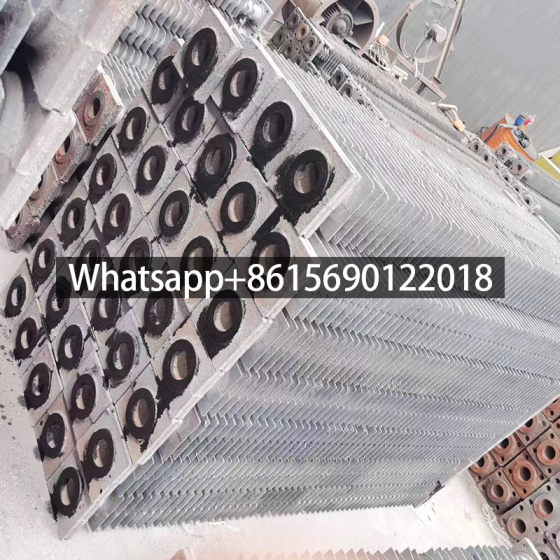
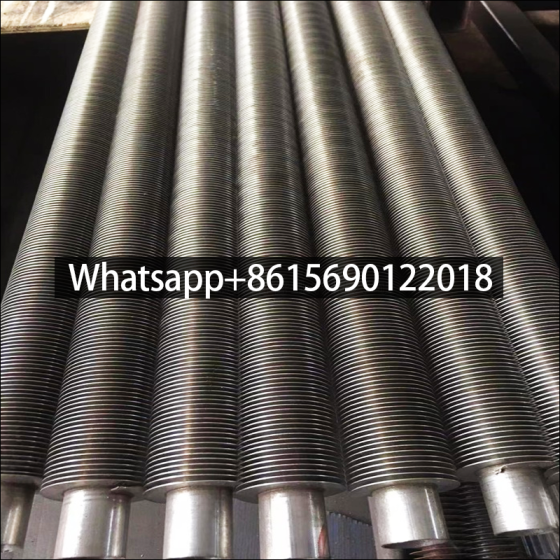
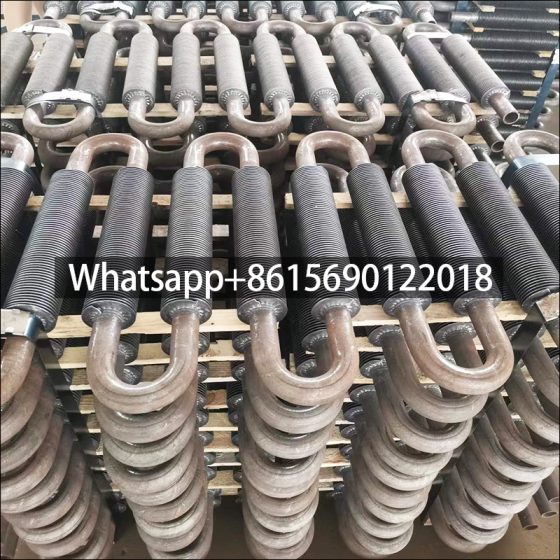
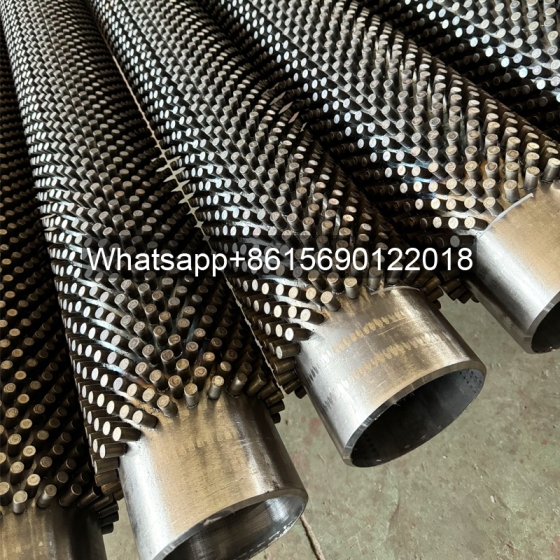
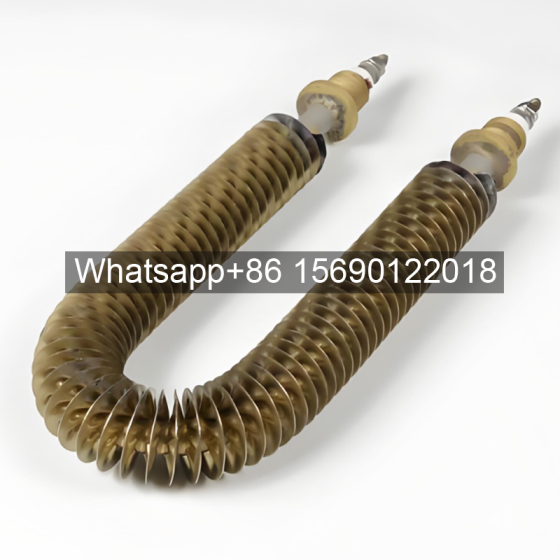
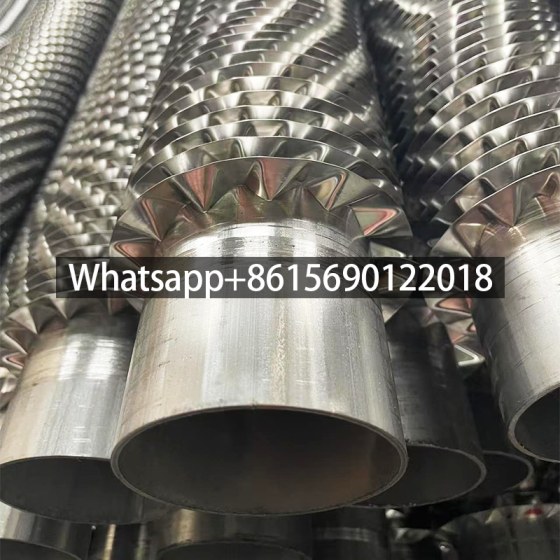
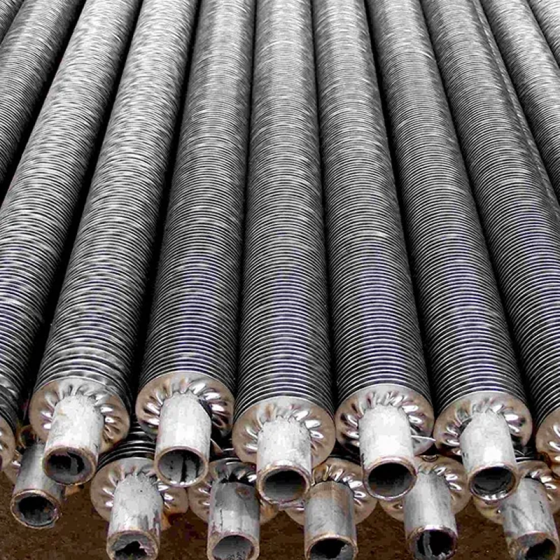
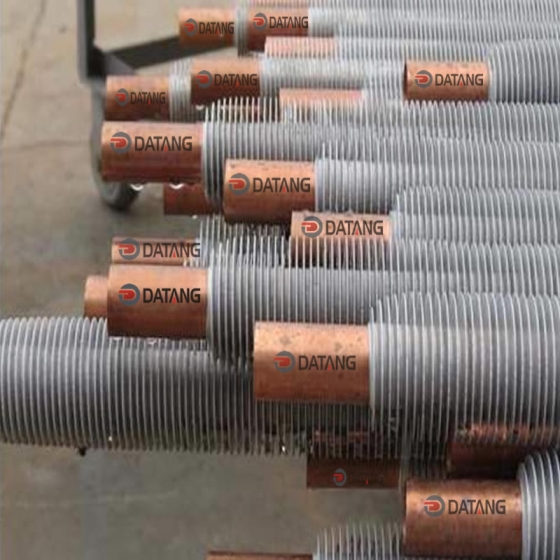
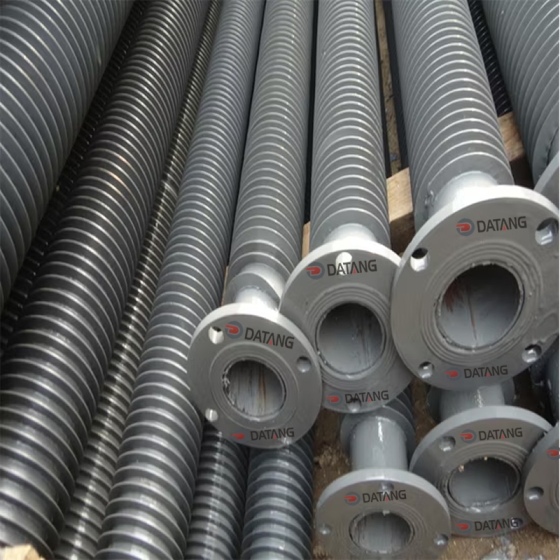
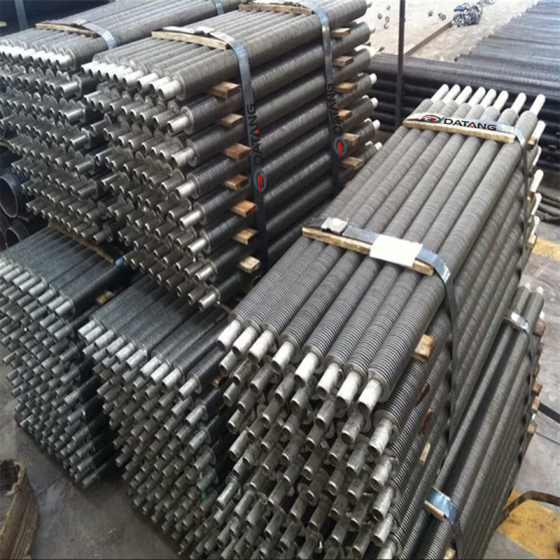
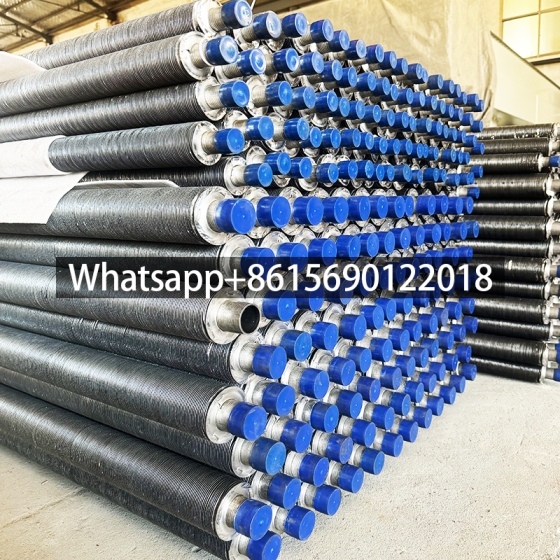
Serpentine finned tubes or bend fin tubes are an important type of heat transfer device used industrial applications, such as boilers and heat exchangers, which bend with fins to increases the surface area of the tube and improves heat transfer.
Products Description
What Are Serpentine Finned Tubes?
Serpentine finned tubes or bend fin tubes are an important type of heat transfer device used in a wide range of industrial applications, such as boilers and heat exchangers. Their unique design, featuring a continuous fin wound and bend in a serpentine shape around the tubes outside surface, increases the surface area of the tube and improves heat transfer between the tube and the surrounding environment.
What The Serpentine Finned Tubes Main Usages?
| Application Category | Key Functionality | Performance Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Small Energy-Saving Devices | Custom-designed serpentine fins optimized for specific size/shape requirements2 | Enhanced heat transfer characteristics for compact systems |
| Renewable Energy Systems | Heat transfer from solar panels/geothermal sources to fluids2 | 40%+ system efficiency improvement with reduced energy consumption |
| Electronics Cooling | Thermal management for high-power components2 | Extended component lifespan through effective heat dissipation |
Serpentine finned tubes are particularly useful in industries where high heat transfer rates are required, such as the petrochemical and power generation industries. They can be used in a variety of heat exchanger designs, such as shell-and-tube or air-cooled heat exchangers, and are often used in applications where space is limited.
Overall, the design of a special serpentine finned tube for small energy-saving devices will depend on the specific application and requirements of the device. However, with careful design and optimization, these tubes can play an important role in improving the efficiency and performance of a wide range of energy-saving devices.
Serpentine Finned Tubes Size:
Serpentine finned tubes are available in a wide range of sizes and fin types to meet different application requirements. The main size parameters for serpentine finned tubes include:
Tube Diameter: The tube diameter is the outer diameter of the base tube, which can range from a few millimeters to several inches depending on the application.
Fin Height: The fin height is the distance between the base tubes outer surface and the highest point of the fin. Fin heights can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
Fin Thickness: The fin thickness is the thickness of the fin material, which can vary depending on the type of fin and the application requirements.
Fin Pitch: The fin pitch is the distance between adjacent fins along the tubes circumference. Fin pitches can vary depending on the application requirements.
The Fin Types Commonly Used In Serpentine Finned Tubes Include:
| Type | Formation Process | Key Features and Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Extruded Fin | Fins are formed by extruding fin material through a die onto the base tube’s outer surface.1 | Results in firm attachment and excellent heat transfer characteristics across diverse industrial systems. |
| L-Foot Fin | Fins are attached using L-shaped feet that are welded or brazed to the tube’s surface.1 | Provides good heat transfer performance and is suitable for high-temperature applications like chemical processing. |
| G-Fin | Fins are shaped by rolling a flat strip into a G-configuration and mechanically attaching to the base tube.2 | Delivers high heat transfer rates and is ideal for compact heat exchangers, optimizing space and efficiency. |
| Knurled Fin | Fins are created by knurling the base tube’s surface to form small ridges, increasing heat transfer area.1 | Suitable for applications requiring high heat transfer rates, such as power generation equipment. |
| HFW Solid Fin | Continuous fins are welded onto the base tube using high-frequency welding.1 | Can be made from materials like carbon steel, alloy steel, or stainless steel, ensuring durability in harsh environments. |
| HFW Serrated Fin | Serrated-edge fins are welded via high-frequency welding, creating turbulence in fluid flow.1 | Enhances heat transfer coefficients and improves overall exchanger efficiency, particularly in energy-intensive setups. |
The choice of the main size and fin type of serpentine finned tubes will depend on the specific application requirements, such as the heat transfer rate, fluid flow rate, and pressure drop.