Aluminum extruded finned tubes, with their high heat transfer efficiency, résistance à la corrosion, and lightweight characteristics, are widely used in the power, chemical, and new energy sectors. Performance is continuously improved through structural optimization and surface treatment technologies, promoting green manufacturing and sustainable development.

The applications of aluminum extruded finned tubes are extremely broad. Their high thermal conductivity makes them a core component of industrial heat exchange equipment.
In the power industry, they are used in boiler waste heat recovery systems, significantly improving the heat exchange efficiency between flue gas and the working fluid by increasing the heat dissipation area. In the chemical industry, their corrosion resistance enables stable condensation or evaporation processes in acidic or alkaline environments. In air conditioning and refrigeration equipment, the lightweight advantage of aluminum finned tubes further reduces system energy consumption.
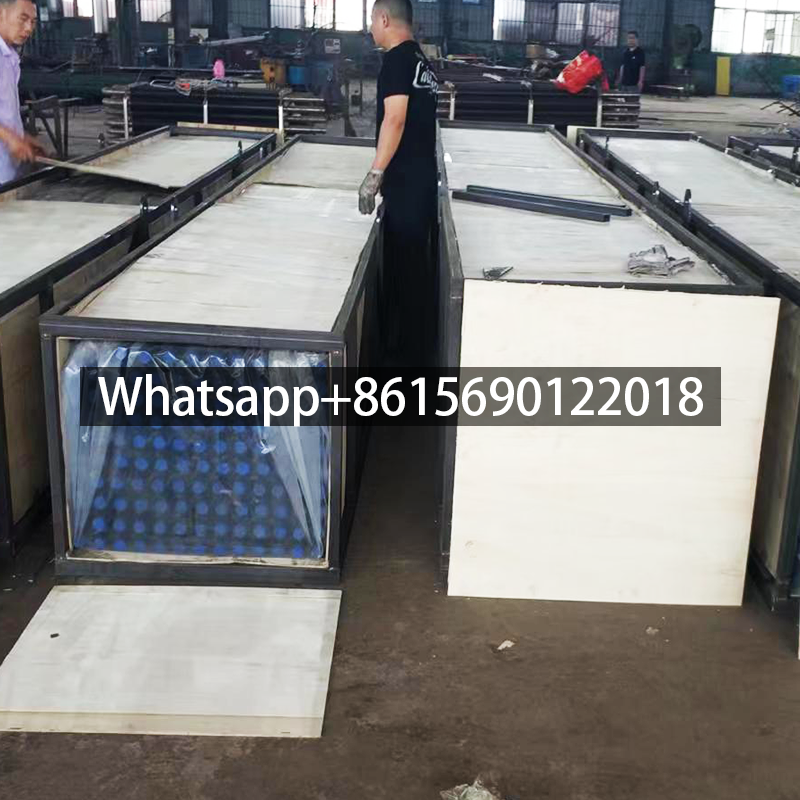
Aluminum extruded finned tubes are a type of finned tube manufacturing process, rolled from aluminum and steel or stainless steel tubes. They feature low contact thermal resistance, high strength, resistance to heat and mechanical vibration, good thermal expansion performance, and a considerable extended heat exchange surface.

The design of aluminum extruded finned tubes is developing towards greater refinement.
Par exemple, by optimizing fin spacing and height, engineers can maximize heat exchange efficiency within a limited space; while the hydrophilic surface coating effectively reduces efficiency losses caused by condensate retention.
In the new energy field, these finned tubes are also integrated into photovoltaic panel cooling systems, increasing solar energy conversion efficiency by more than 12% through active heat dissipation.
Customized irregular-shaped finned tubes will become possible.
This structure can overcome the limitations of traditional extrusion processes, further perturbing the fluid boundary layer through biomimetic design (such as fractal structures or vortex-induced textures), resulting in a breakthrough increase in heat transfer coefficient. Simultaneously, the large-scale application of recycled aluminum materials will drive the low-carbon transformation of the entire industry chain, enabling efficient heat transfer and sustainable development to coexist synergistically.

 dtfinnedtube.com
dtfinnedtube.com