What is a finned tube radiator?
Finned tube radiators are used in various industries, including textiles, printing and dyeing, petroleum, chemical engineering, drying, and power generation.

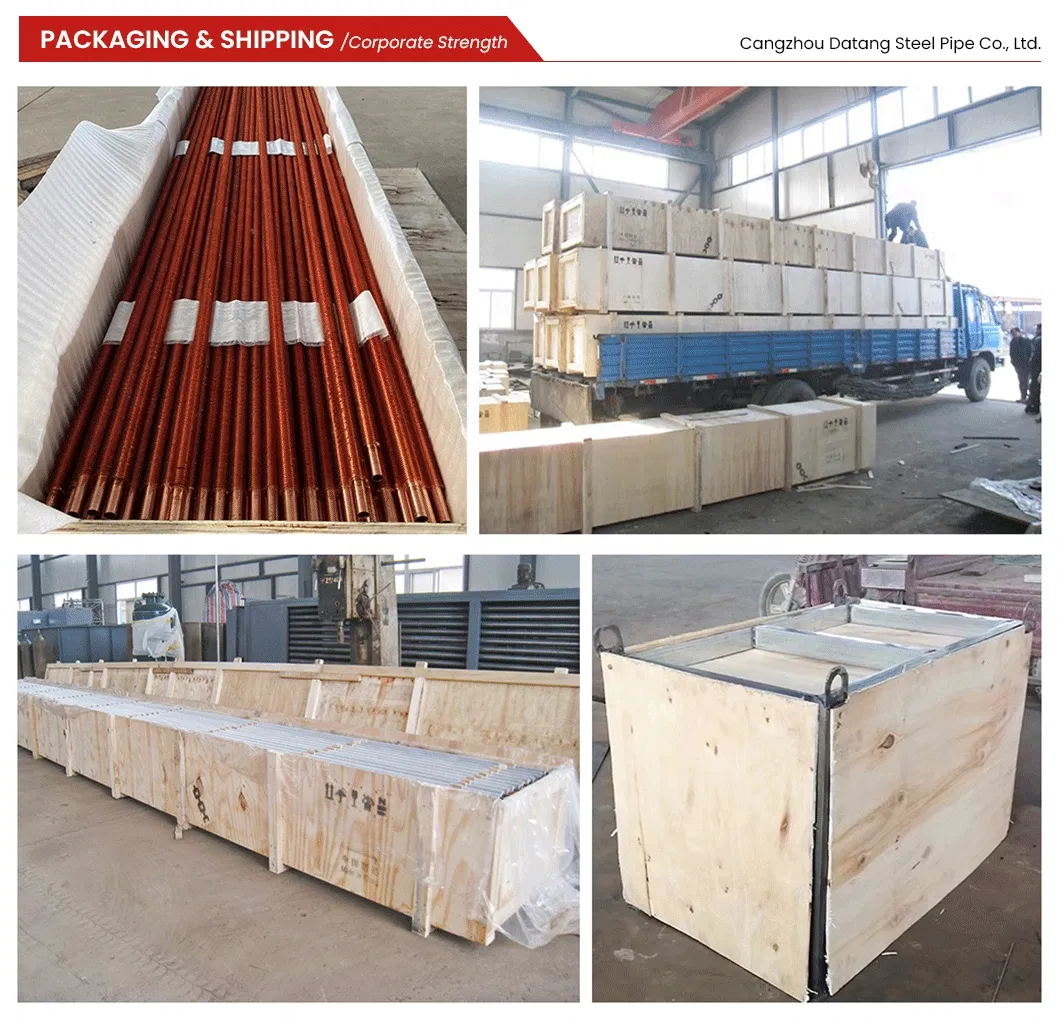
Finned Tube Radiators Manufacturer and Supplier
Finned tube radiators are the most widely used type of heat exchanger for gas and liquids. They enhance heat transfer by adding fins to a standard base tube. The base tube can be made of steel, em aço inoxidável, or copper, and the fins can be made of steel, em aço inoxidável, copper, or aluminum strips. The fin structure increases the heat dissipation area, achieving efficient heat transfer. Finned tube radiators are categorized by fin structure: wound fin, string fin, welded fin, and rolled fin. Steel-aluminum finned tubes combine the pressure resistance of steel tubes with the high thermal conductivity of aluminum.
Structural Principle of Finned Tube Radiators
Any heat exchanger that adds fins to the heat exchange tubes to increase the heat dissipation area is generally referred to as a “finned tube radiator.”
Finned tube radiators are categorized by fin structure as wound fin, string fin, welded fin, or rolled fin. Common materials include steel, em aço inoxidável, copper, and aluminum.
Fin Tube Radiator Applications
The most widely used finned radiator is the steel-aluminum finned tube (wound-type steel-aluminum composite finned tube and rolled-type steel-aluminum composite finned tube). These utilize the pressure resistance of steel tubes and the high thermal conductivity of aluminum, composited on specialized machine tools. Their contact thermal resistance is virtually zero at 210°C.
Steel-aluminum composite tube radiators offer advantages unmatched by other finned tube radiators.
Fin tube radiators are generally used for heating or cooling air and feature a compact structure and large unit heat exchange area. They are widely used in various industries, including textiles, printing and dyeing, petroleum, chemical, drying, and power generation.





 dtfinnedtube.com
dtfinnedtube.com