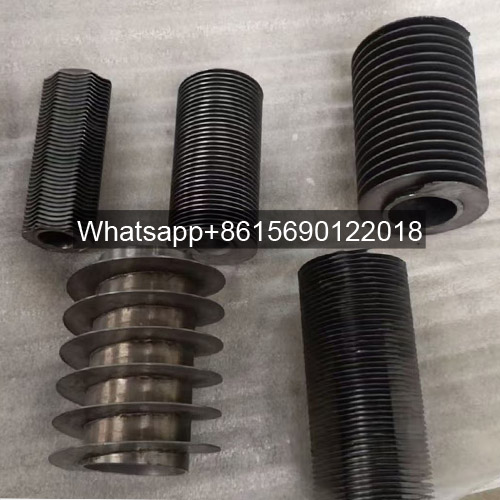
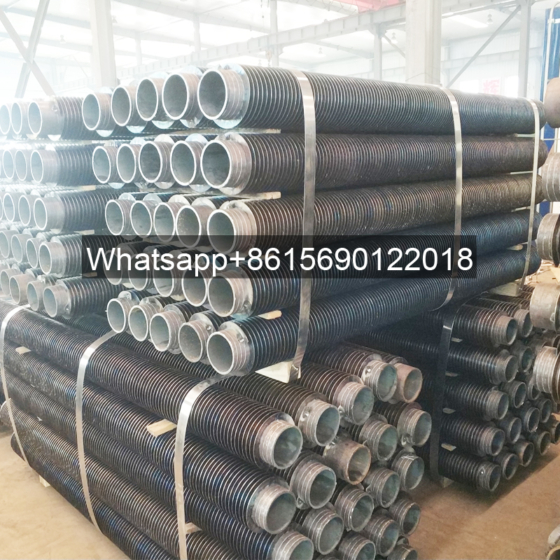
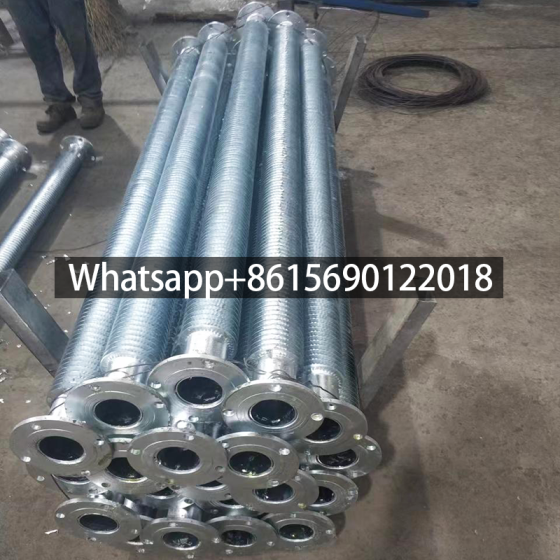
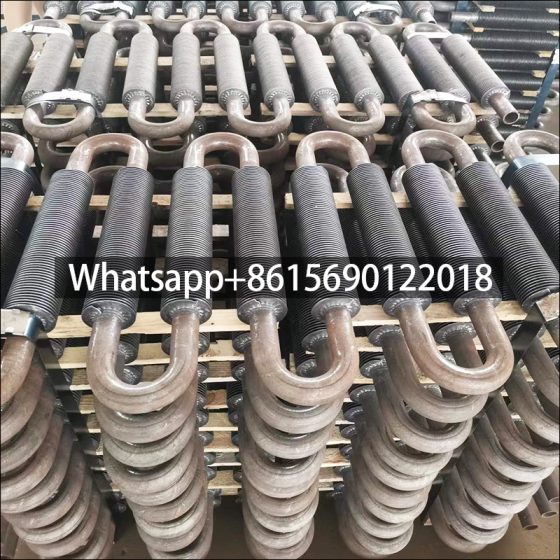
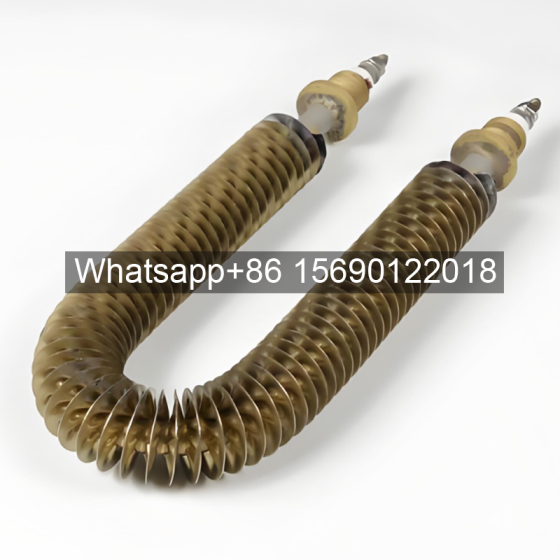
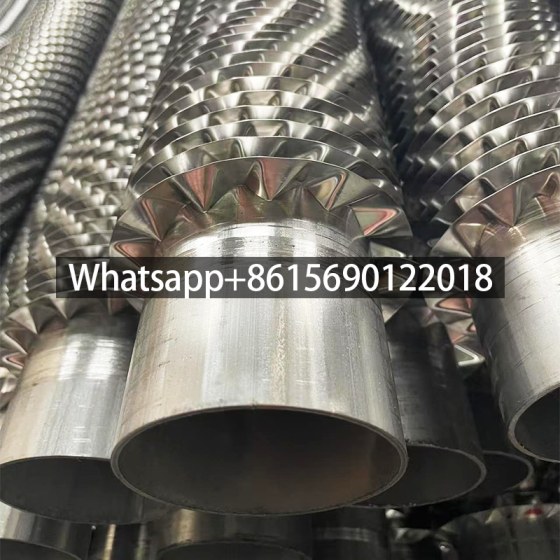
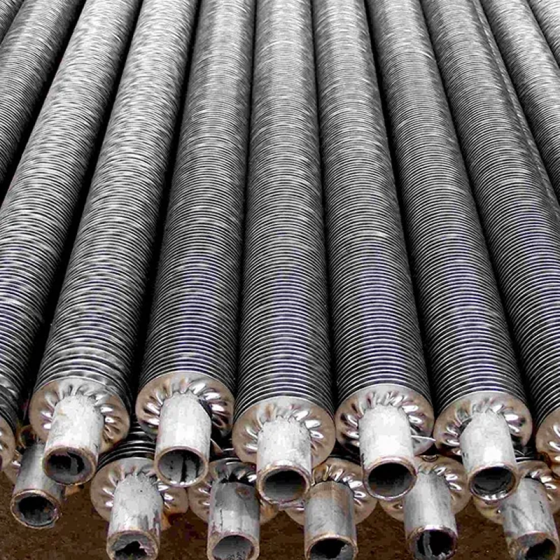
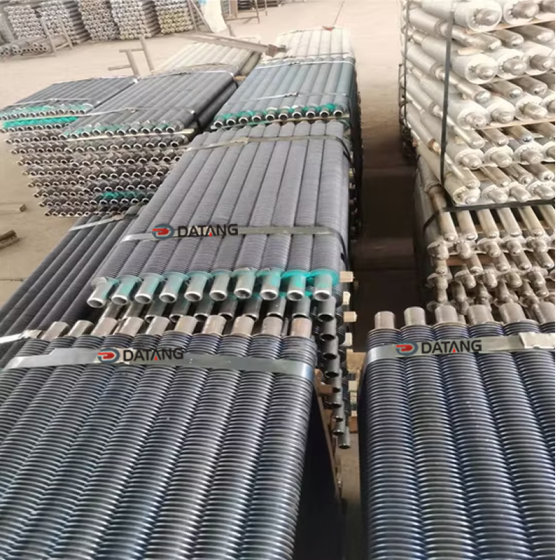
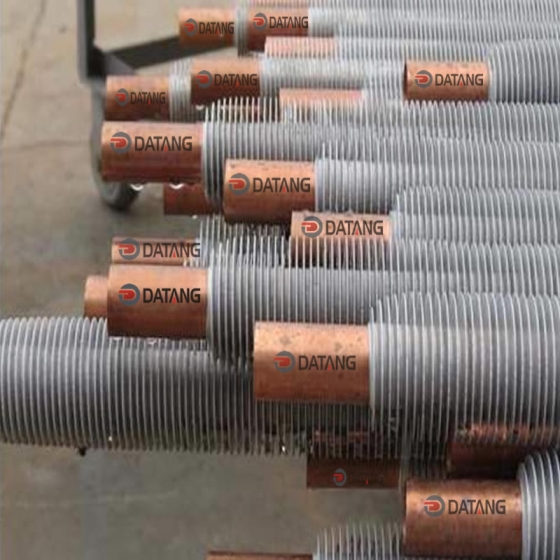
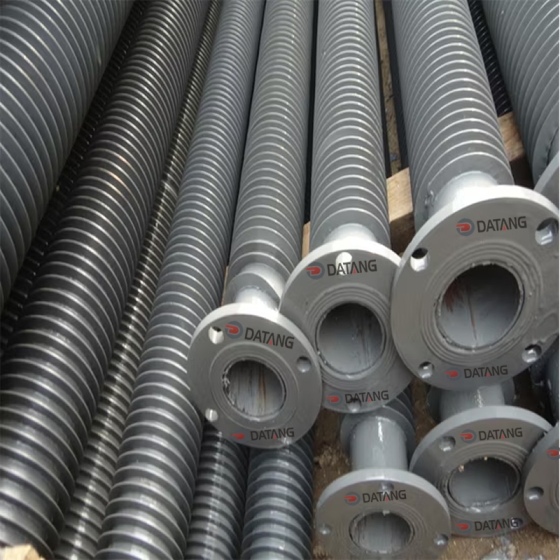
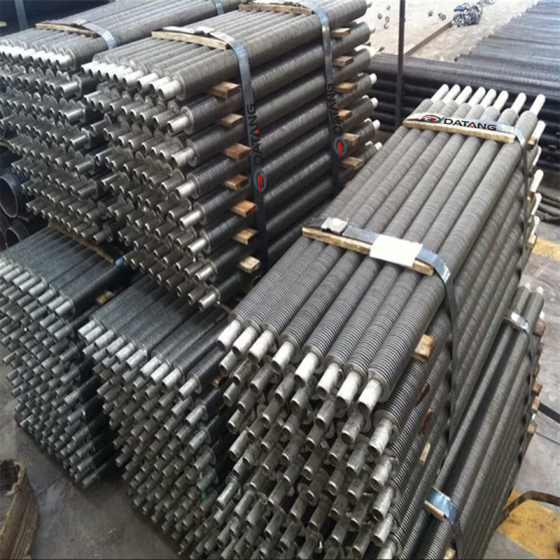
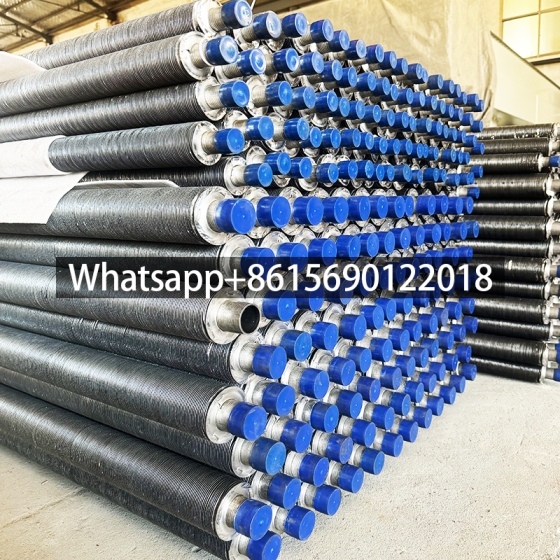
A gilded tube is a heat exchange element used for heat exchange, which enhances heat transfer efficiency by increasing the outer surface area of the tube. Its core structure involves creating fins on the surface of a base tube through welding, rolling, or embedding processes, thereby significantly expanding the heat transfer area.
During operation, two fluids at different temperatures flow inside and outside the tube, respectively. The fluid inside the tube transfers heat through the base tube, while the fins on the outside enhance the turbulence and heat exchange of the fluid outside the tube, allowing for efficient heat transfer between the two fluids.
Key Features of Gilled Tube
Structural Design: The finned tube consists of a base tube and fins. The fins effectively increase the heat transfer area of the copper tube, thereby improving heat transfer capacity.
Working Principle: Heat is conducted from the fluid inside the tube to the tube wall, and then transferred to the fluid outside the tube (such as air) through the fins. The two fluids do not directly contact each other.
Application Advantages: Particularly suitable for gas heat exchange scenarios, as the convective heat transfer coefficient of gas is relatively low. The fins can increase the heat transfer area and enhance turbulence, thereby increasing the heat transfer rate.
Typical Applications of Gilled Tubes
Industrial Applications: Widely used in heat exchange systems in industries such as petroleum, chemical, and power, including air coolers and boiler waste heat recovery.
Consumer Applications: Commonly found in radiators for air conditioners, refrigerators, and other equipment.
Gilled Tubes solve the problem of limited heat exchange area in traditional bare tubes through structural optimization, making them a key component in both industrial and consumer heat exchange systems.
The choice of material for a Gilled Tube depends primarily on the combination of the base tube and fins. Different materials have different characteristics in terms of thermal conductivity, resistência à corrosão, pressure resistance, and cost. The following are common material types and their applicable scenarios:
Gilled Tube Base Tube Materials
Aço carbono: Thermal conductivity between 46-58, high carbon content, good thermal conductivity rate, relatively stable price, and high cost-effectiveness.
Aço inoxidável (por exemplo,, 304/316L): Strong corrosion resistance, suitable for corrosive environments (such as chemical plants and humid areas), but higher cost.
Copper: With a thermal conductivity as high as around 400, it boasts the highest thermal conductivity, but is expensive and primarily used in demanding applications.
Aluminum: Lightweight, with fast thermal conductivity and a lower price, but has weaker pressure resistance, suitable for budget-constrained or lightweight applications.
Gilded Tube Fin Materials
Steel Fins: Combined with steel pipes (por exemplo,, high-frequency welded finned tubes), they offer strong welds, long lifespan, and are suitable for industrial plants and commercial heating.
Aluminum Fins: Often combined with steel pipes (por exemplo,, steel-aluminum composite finned tubes), utilizing aluminum’s high thermal conductivity, resulting in low contact thermal resistance and uniform heat dissipation.
Galvanized Fins: Excellent corrosion resistance, affordable price, suitable for humid environments (por exemplo,, livestock sheds, residential heating).
Gilded Tube Composite Materials
Bimetallic Rolled Finned Tube: Seamless bonding between the base tube and fins (por exemplo,, carbon steel pipe rolled aluminum fins), lightweight, and provides uniform heat dissipation, suitable for demanding applications such as drying and waste heat recovery.
Steel-aluminum composite finned tubes: Combining the pressure resistance of steel and the thermal conductivity of aluminum, they offer low contact thermal resistance and superior overall performance.
Gilded Tube Selection Recommendations
Corrosive environments: Stainless steel or galvanized finned tubes are preferred.
High thermal conductivity requirements: Consider copper tubes or aluminum finned tube combinations.
Limited budget: Aluminum finned tubes or carbon steel base tubes are economical options.
 dtfinnedtube.com
dtfinnedtube.com