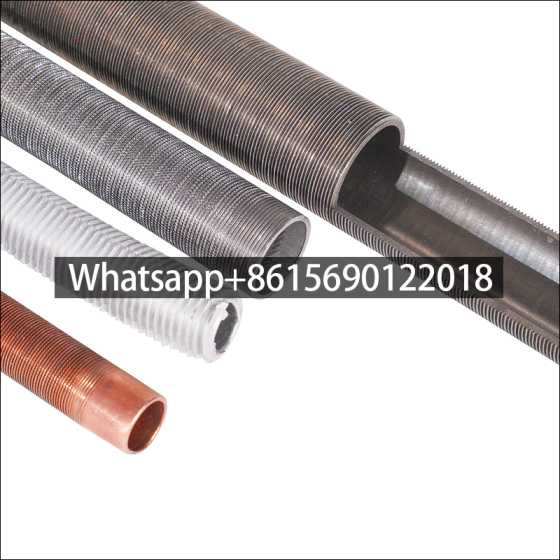
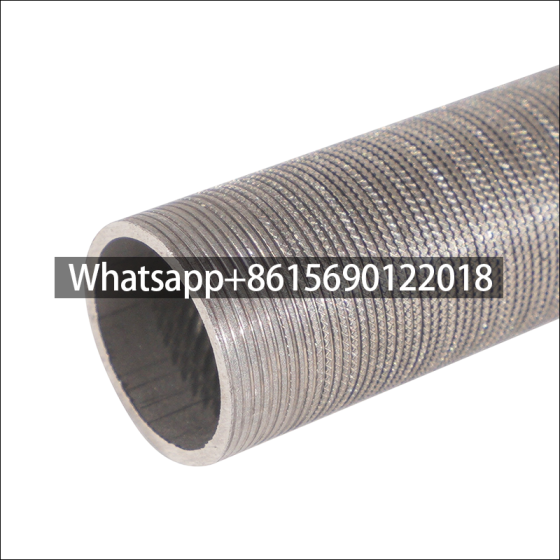
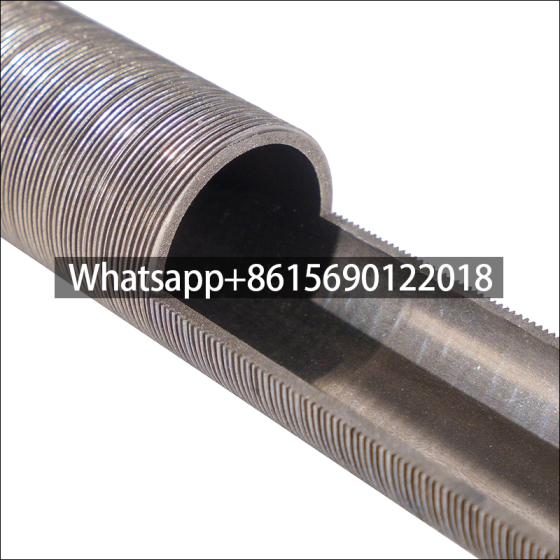
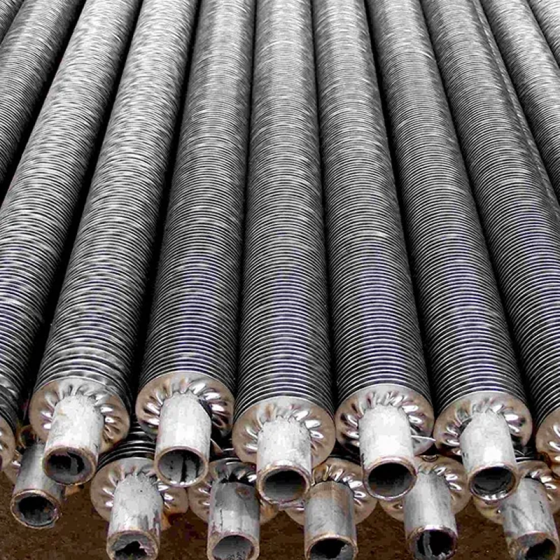
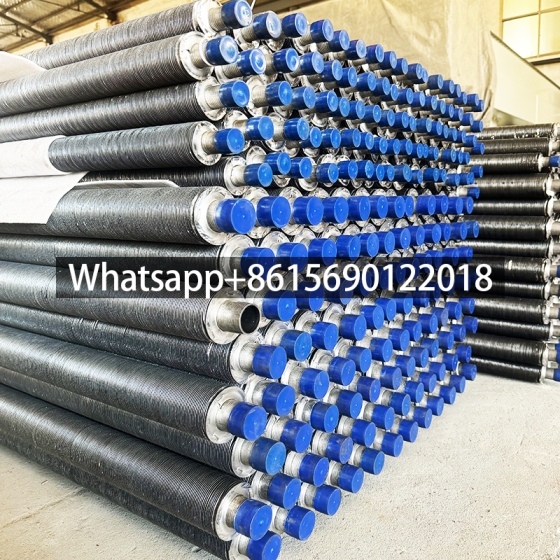
Low fin tube production method
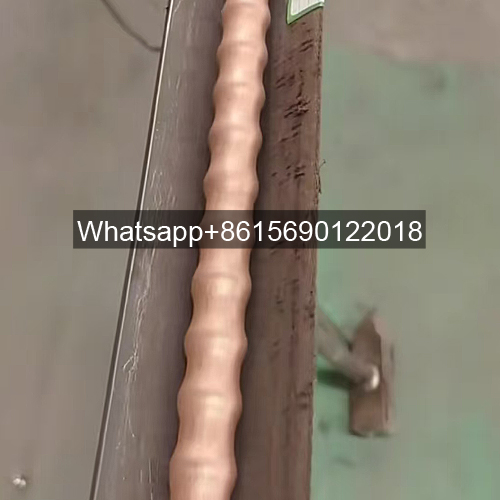
Rolling method (three-roller oblique rolling): Low fin tubes are usually produced by rolling method. In this method, a core rod is lined inside the bare tube, and the tube material moves in a spiral linear motion under the drive of the roller blade, and the fins are gradually processed on its outer surface through the hole type composed of the roller groove and the core rod.
In order to facilitate the fin forming, the rolled piece adopts three stages of biting, rolling and shaping during the deformation process, so that the processed fins are complete, smooth and regular. The fin tube produced by this method has no contact thermal resistance loss and electrical corrosion problems because the base tube and the outer fin are an organic whole, and has good heat transfer efficiency and strong anti-deformation ability.
Uses of low fin tubes:
Due to its excellent heat exchange performance, low fin tubes are widely used in condensers, evaporators and other equipment of air conditioners, and are an important part of these equipment.
Material Selection Basis for Condenser Fin Tubes
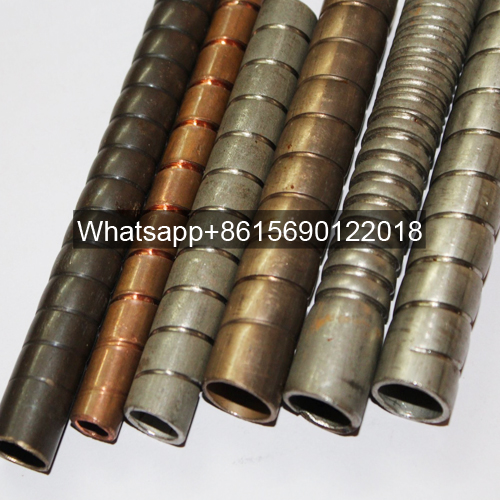
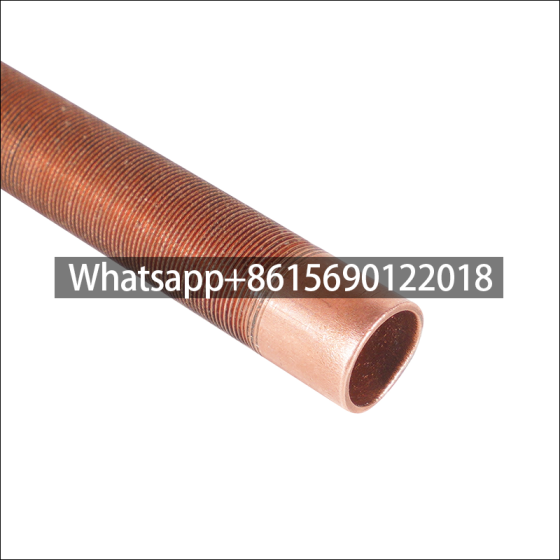
1. Copper Low-Fin Tubes
- Thermal Conductivity: Copper’s thermal conductivity (400 W/m·K) is 20× higher than stainless steel, significantly enhancing heat transfer efficiency.
- Cost-Effectiveness: 30-50% cheaper than stainless steel, ideal for conventional water-cooled condensers.
- Limitations: Prone to erosion corrosion at flow velocities >2.5 m/s and vulnerable to ammonia environments.
2. Stainless Steel Low-Fin Tubes
- Corrosion Resistance: 316L stainless steel exhibits ≤0.1 mm/year corrosion rate in seawater, suitable for marine/chemical applications.
- Mechanical Strength: Yield strength (≥205 MPa) doubles copper’s, withstanding 4 MPa working pressure.
- Special Applications: Mandatory in food/pharmaceutical industries per FDA/GB standards.
3. Decision-Making Matrix
CriteriaCopperStainless SteelInitial Cost$50/m$120/mService Life5-8 years15+ yearsMaintenance CycleAnnualBiannual
Conclusion: Copper tubes optimize operational costs in freshwater systems, while stainless steel ensures reliability in corrosive/sterile environments. Hybrid solutions (copper core with stainless cladding) are emerging for balanced performance.
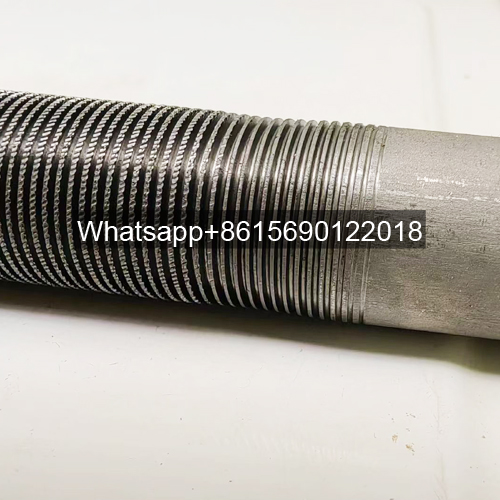
1. Low Fin Tube Basic Processing Dimensions & Parameters
| OD (mm) | Wall Thickness (mm) | Fin Pitch (mm) | Fin Height (mm) | Min. Wall Thickness after Grooving (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ф16 | 1.2 | 0.8-1.33 | 0.8-1 | 0.8 |
| Ф16 | 2 | 0.8-1.45 | 1.6-1.2 | – |
| Ф19 | 2.1 | 1-1.45 | 1.6-1.2 | 2.77 |
| Ф19 | 2.3-1.6 | – | – | – |
| Ф25 | 2 | 1.5-1.2 | – | 2.77 |
| Ф25 | 2.3-2.1 | – | – | – |
| Ф28 | 2.77 | – | – | 2.5-2.1 |
Note: These are standard parameters. Custom designs are available based on client requirements1.
2. Low-Fin Tube Size & Heat Exchange Area Table
a) OD 19mm
| Materiale | Fin Pitch (mm) | Fin Height (mm) | Surface Area (m²/m) | Fin Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acciaio inossidabile | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.134 | 2.23 |
| Acciaio inossidabile | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.147 | 2.45 |
| Acciaio inossidabile | 1.3 | 1.30 | 0.164 | 2.73 |
| Carbon Steel | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.168 | 2.80 |
| Carbon Steel | 1.3 | 1.5 | 0.178 | 2.97 |
| Bare Tube (Smooth) | – | – | 0.060 | – |
b) OD 25mm
| Materiale | Fin Pitch (mm) | Fin Height (mm) | Surface Area (m²/m) | Fin Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acciaio inossidabile | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.180 | 2.25 |
| Acciaio inossidabile | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.199 | 2.49 |
| Acciaio inossidabile | 1.3 | 1.30 | 0.223 | 2.79 |
| Carbon Steel | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.227 | 2.84 |
| Carbon Steel | 1.3 | 1.5 | 0.243 | 3.04 |
| Bare Tube (Smooth) | – | – | 0.080 | – |
Advantages of low fin tubes
High heat exchange efficiency: Due to the presence of fins, low-fin tubes have a larger surface area and can achieve higher heat exchange efficiency with the same metal material consumption.
Strong anti-deformation ability: The low-fin tubes produced by the rolling method have a base tube and an outer fin tightly combined as a whole, so that the fin tubes have good anti-deformation ability during use.
No contact thermal resistance and electrical corrosion problems: Since there is no need for welding or other connection methods between the base tube and the outer fin, there is no problem of contact thermal resistance and electrical corrosion.
Low-fin tubes are a heat exchange element with excellent heat exchange performance, strong anti-deformation ability and long service life. They play an important role in air conditioner condensers, evaporators and other equipment.
 dtfinnedtube.com
dtfinnedtube.com