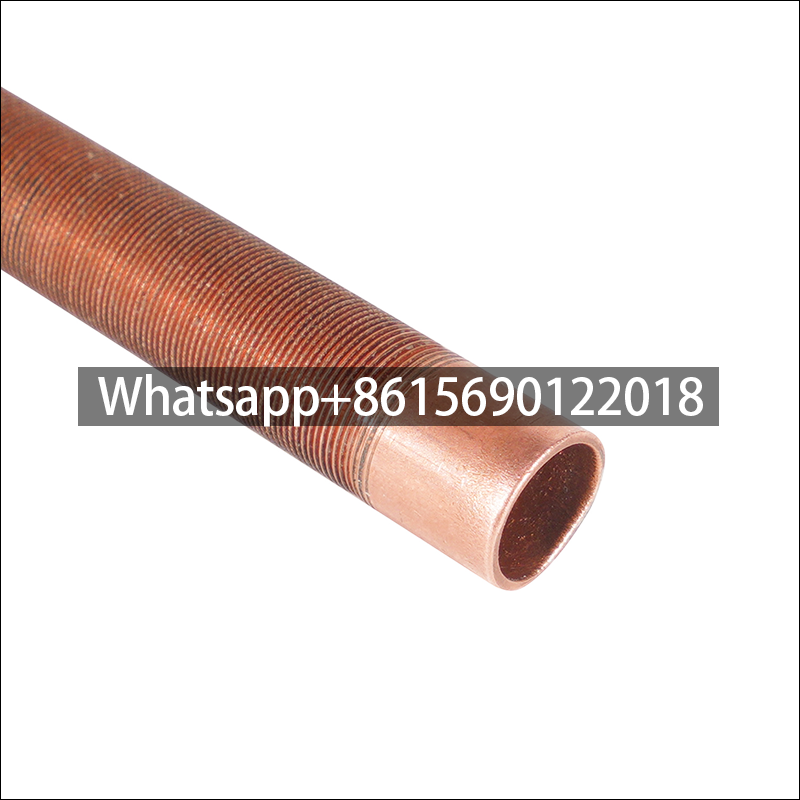
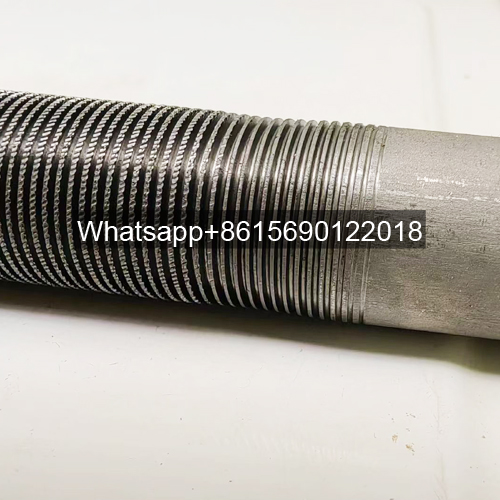
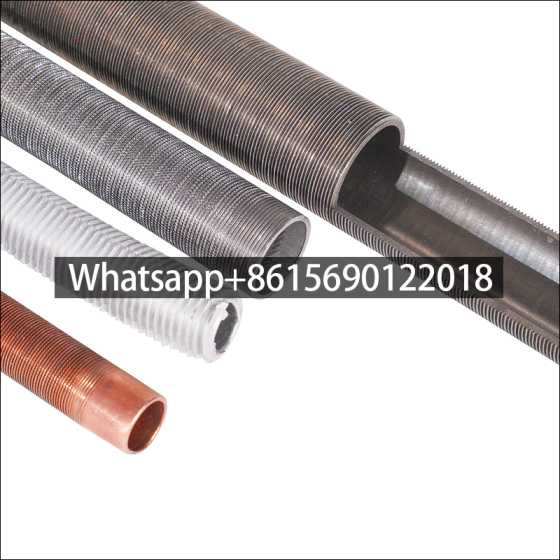
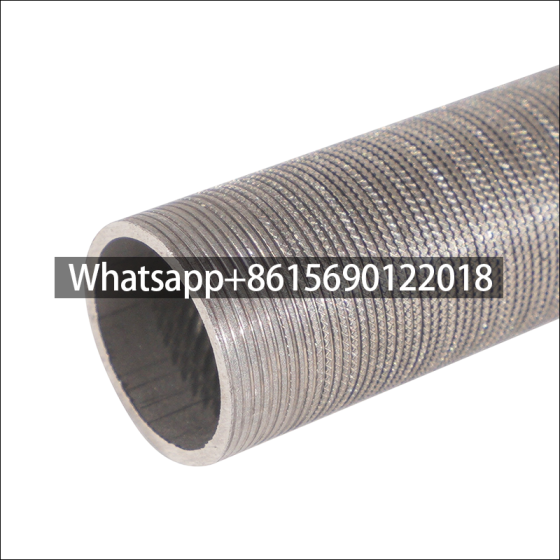
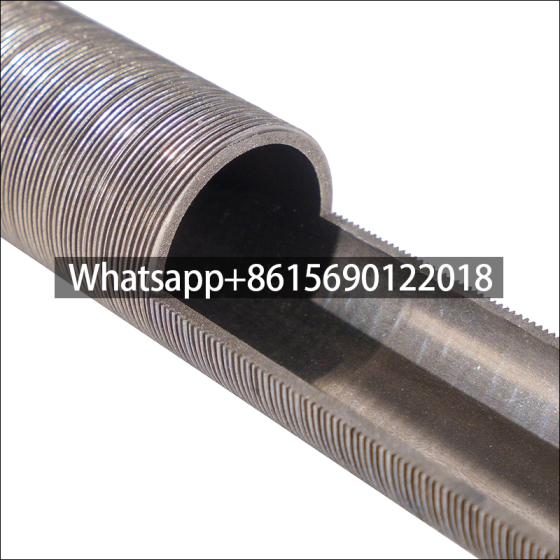
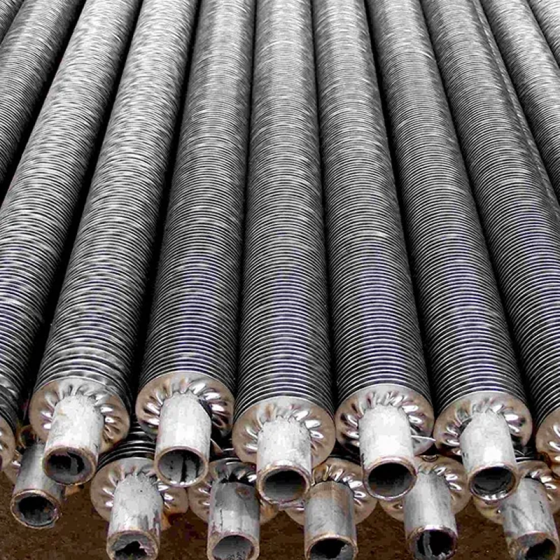
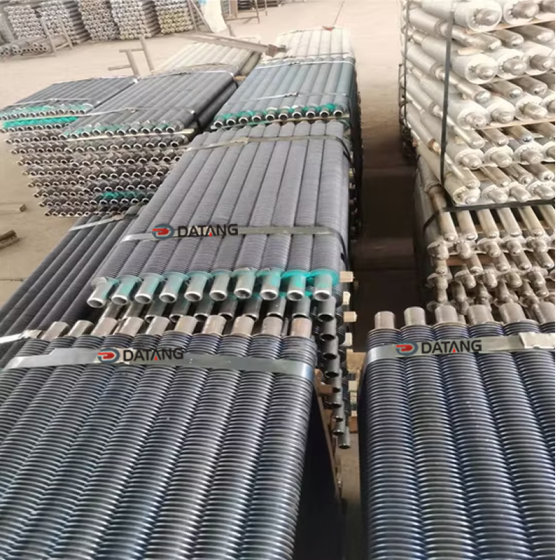
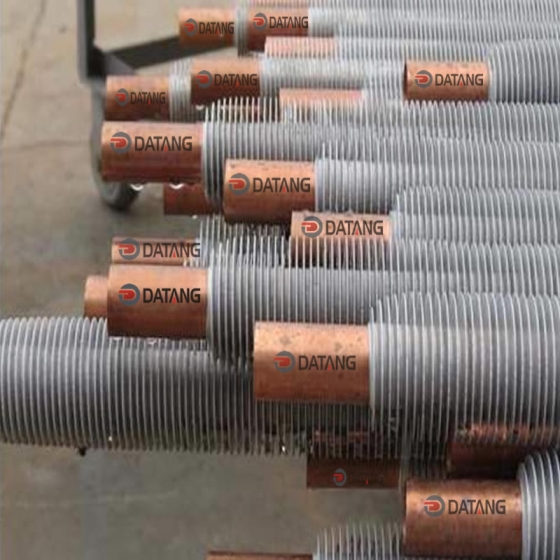
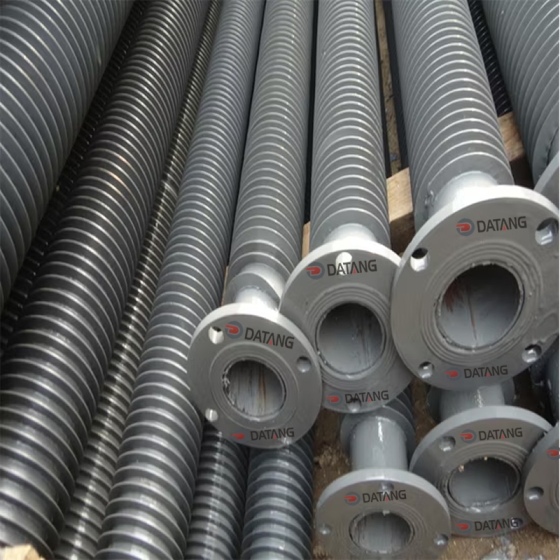
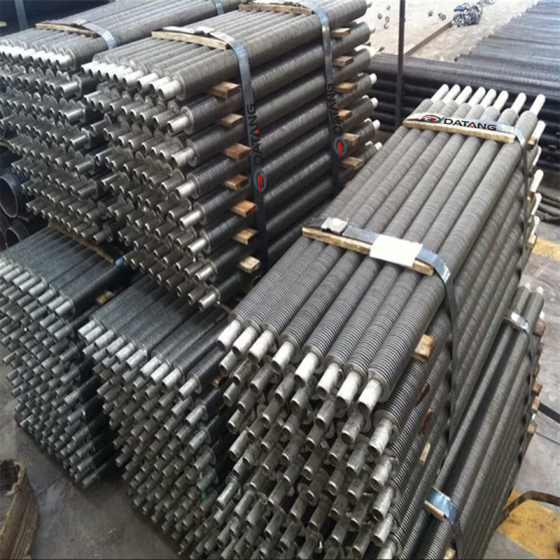
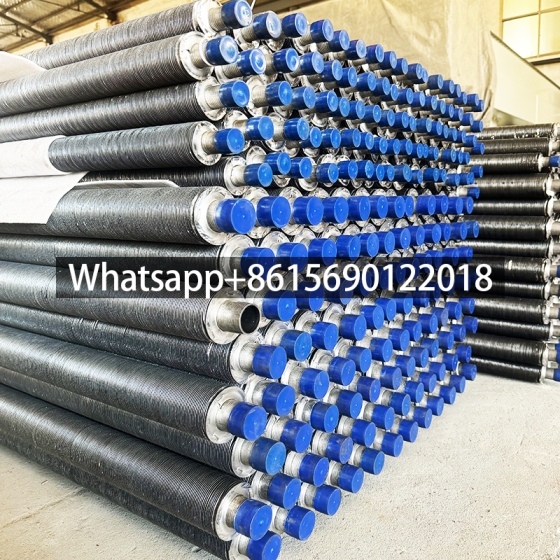
Low fin tube is a heat exchange element that forms continuous spiral fins on the outer surface of the light tube through mechanical processing. It is mainly used in condensers, evaporators and other equipment of air conditioners to improve heat exchange efficiency.
Structure and process of low fin tube
The surface fins are processed by rolling method (three-roller oblique rolling). The base tube and the outer fins are tightly integrated into one, without contact thermal resistance or electrical corrosion problems, and have high anti-deformation ability.
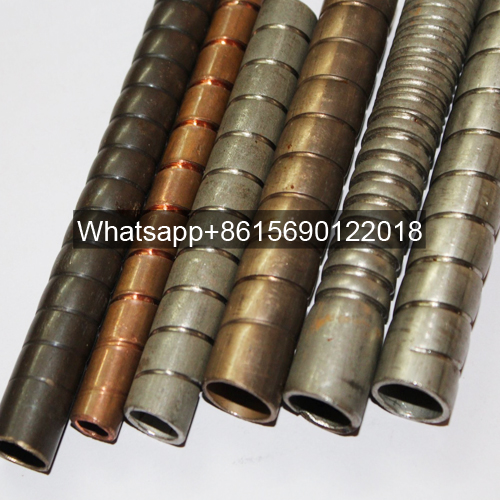
Materials and Specifications for Low Fin Tubes
| Category | Materials | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| Base Tube | • Carbon steel (10#, 20#) • Stainless steel (304, 316L, 2205) • Duplex steel/Titanium |
• OD: 16–28 mm • Wall thickness: 1.2–2.77 mm |
| Fin | • Aluminum (1060, 1100) • Copper/Steel |
• Height: 0.8–1.45 mm (typically ≤1.5 mm) • Pitch: 0.8–1.33 mm |
| General Parameters | • Wall thickness after finning: 0.8–2.5 mm • Pressure rating: ≤6 MPa |
|
Key Notes:
- Material Combinations:
- Carbon steel tube with aluminum fins: Cost-effective solution for general industrial use.
- Stainless steel/Titanium tubes: Essential for corrosive or high-temperature environments.
- Customization:
- Fin pitch and height adjustable to optimize heat transfer efficiency or reduce fouling.
- Typical Applications:
- Condensers, evaporators, and chemical processing heat exchangers.
Main advantages of low fin tube
High heat exchange efficiency: The fins increase the surface area of the tube and achieve higher heat exchange efficiency under the same metal consumption.
Stable structure: The base tube and the fin are integrated into one design, with strong anti-deformation ability and long service life.
Applicable scenarios of low fin tubes
Mainly used in the condenser of air conditioning refrigeration system, reducing energy consumption by enhancing heat exchange.
 dtfinnedtube.com
dtfinnedtube.com