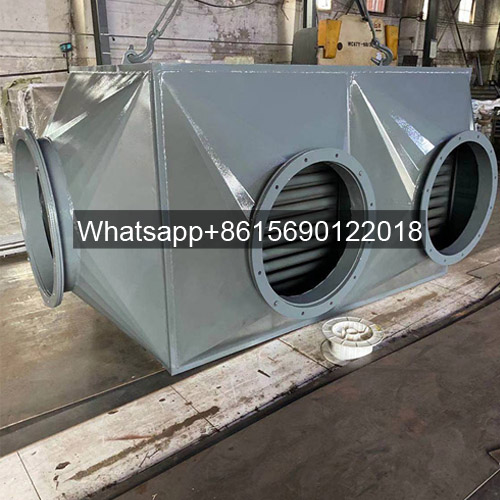
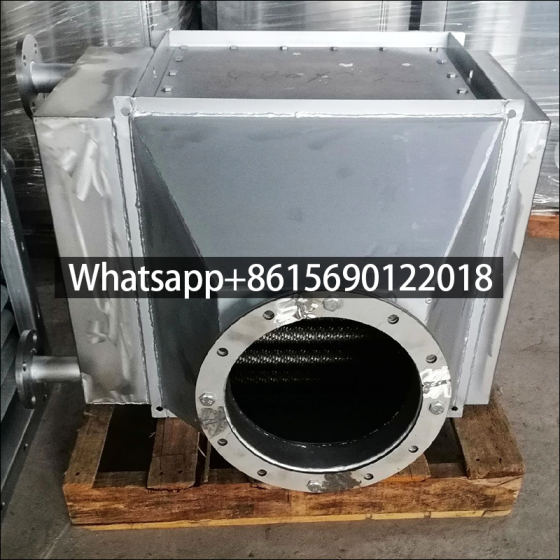
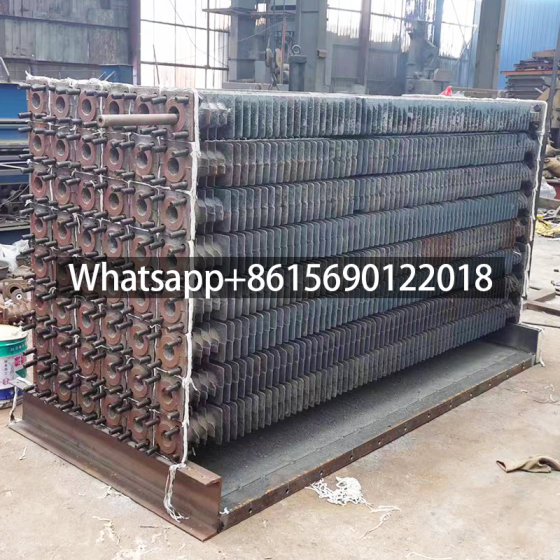
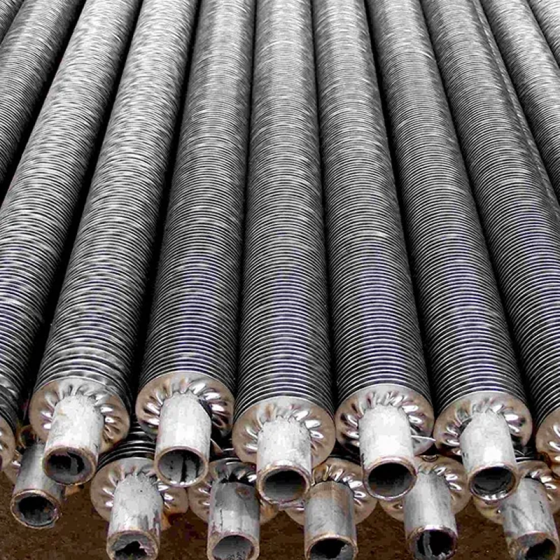
Cast Iron Economizer for Flue Gas Heat Recovery Equipment
The economizer is a component that recovers the heat of the low-temperature flue gas at the tail of the boiler to heat the feed water. For hot water boilers or steam boilers, the economizer has actually become a part of the heating surface of the boiler body, but it is still customarily called an economizer.
Economizers can be divided into cast iron economizers and steel tube economizers according to different manufacturing materials.
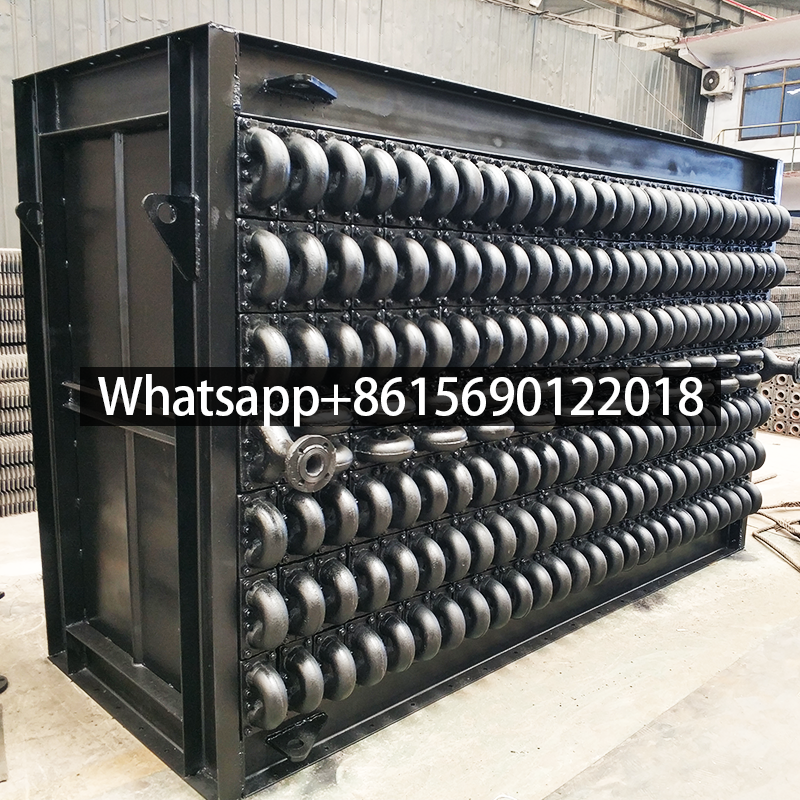
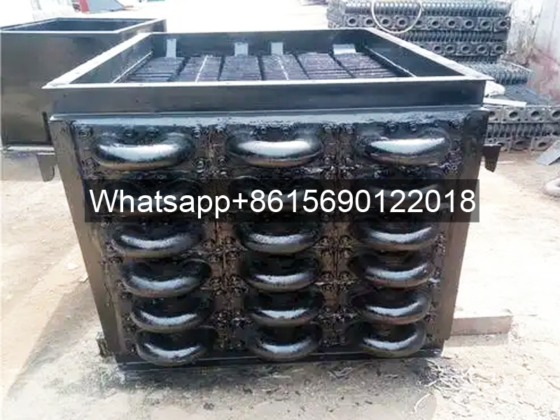
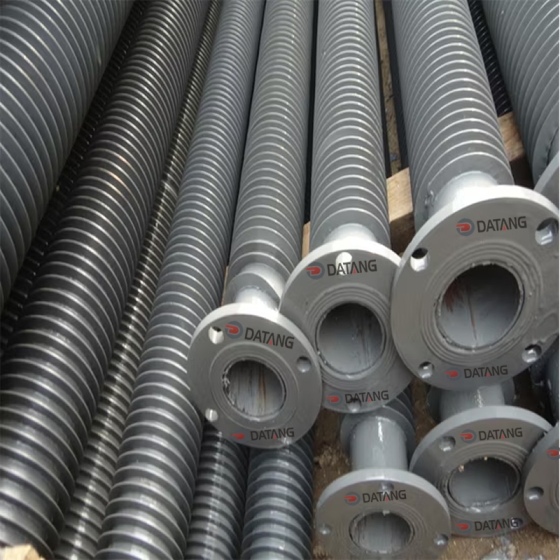
The cast iron economizer is composed of many cast iron pipes with fins and cast iron elbows. The system return water flows from bottom to top in the economizer tube, and the flue gas flows from top to bottom outside the tube.
The advantages of cast iron economizers are large heating area, low maintenance cost, and especially good corrosion resistance, and they are widely used in small boilers. The disadvantages are that ash is easily accumulated between the fins, the flue gas resistance is large, the compressive strength is low, and the outlet water temperature cannot be too high and must be lower than the saturated water temperature.
What is a cast iron economizer?
The cast iron economizer consists of a series of cast iron pipes with square fins on the outside connected in series by 180° cast iron elbows.
Water enters from one end of the lowest layer of pipes, flows horizontally back and forth to the last pipe on the other side, and then enters the upper layer of pipes, flowing from bottom to top. Flue gas flows from top to bottom, forming a countercurrent heat exchange with the water flow. Generally, the water flow rate is not less than 0.3m/s, so that gases such as O2 and CO2 generated during the heating of feed water can be carried away with the water flow. The advantages of cast iron economizers are corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
Small-capacity low-pressure boilers generally do not have good feed water deoxygenation equipment, and oxygen corrosion is prone to occur inside; at the same time, because the water temperature is very low when the feed water enters the economizer, the outer wall of the pipe is prone to condensation, and SO3 in the flue gas combines with water vapor to form When the acid mist reaches the dew point, acid liquid is formed on the outer wall of the tube, causing external acid corrosion.
Most small-capacity low-pressure boilers use cast iron economizers. However, the strength of cast iron economizers is not high, that is, the pressure bearing capacity is low (not more than 2.4MPa). Low-pressure boilers with larger capacity and boilers with medium parameters or above generally use steel tube economizers.
1. Introduction to cast iron economizers
The cast iron economizer is a device used to reduce the amount of coal burned. Its principle is to increase the contact area between the flue gas and the air by swirling the flue gas in the flue, thereby increasing the combustion efficiency of the coal gas and reducing the consumption of coal. At the same time, it can also reduce the emissions in the flue gas.
2. The principle of cast iron economizers
The main principle of cast iron economizers is to use the inertia of flue gas movement to form a vortex in the flue, so that the flue gas and air are fully mixed, thereby achieving full combustion and reducing coal consumption. Another advantage of cast iron economizer is that it can improve the flow of flue gas, make it smoother, prevent smoke from depositing in the flue gas, and reduce the condensation of flue gas and prevent condensation in the flue gas.
3. Advantages of cast iron economizer
The main advantage of cast iron economizer is that it can reduce the amount of coal burned, save energy and reduce consumption, and at the same time reduce the emission of harmful gases such as carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides produced in flue gas, and reduce environmental pollution. In addition, cast iron economizer has the characteristics of good thermal stability, long service life and easy installation.
4. Application scope of cast iron economizer
Cast iron economizer is mainly suitable for various coal-fired equipment such as boilers, industrial furnaces, kilns, etc., and its application field is very wide. In China, due to the promotion of environmental protection policies, the domestic market demand for cast iron economizers continues to grow, and it is expected to have broad market prospects in the future.
Cast iron economizer is a very useful equipment that can effectively reduce the amount of coal burned, reduce environmental pollution, and has a very wide range of applications and long-term market prospects.
The disadvantage of cast iron economizer is that it cannot be made into boiling type. Otherwise, water hammer is easy to occur, which will damage the economizer; the tube wall of cast iron economizer is thick, and the volume and weight are large; ash is easy to accumulate and block between fins; elbows are prone to water seepage and leakage.
Because cast iron is brittle and has poor impact resistance, it is necessary to prevent water from vaporizing in cast iron economizer and causing water hammer. Therefore, cast iron economizer is also called non-boiling economizer, and its outlet water temperature should be at least 30-40℃ lower than the saturation temperature under the corresponding pressure to ensure safety and reliability.
Cast iron economizer has been serialized and can be selected according to relevant manuals during design. The heat release coefficient of water in the medium in the tube is very large, and the flow rate has little effect. The smoke velocity flowing through the economizer (lateral flushing) should be 6-9m /s to avoid serious ash accumulation. In order to ensure the cleanliness of the heating surface, a soot blower needs to be arranged. It is best to have a bypass flue and a bypass waterway for the waterway.
In order to ensure and supervise the safe operation of the cast iron economizer, various instrument accessories are installed on its inlet and outlet pipelines. The safety valve is installed at the inlet to avoid water hammer in the water supply pipe, the safety valve is installed at the outlet to release pressure during vaporization and overpressure, and the vent valve is used to remove air during startup. The pipeline must also consider the economizer damage, water leakage, and maintenance during boiler operation, isolate the economizer, and feed water directly into the boiler drum.
When the boiler is ignited and shut down, no water is fed, but the high-temperature flue gas still flows through the economizer to vaporize the water. In order to avoid vaporization, the cast iron economizer is often equipped with a flue gas bypass.
When the boiler is started, the high-temperature flue gas flows through the bypass flue instead of the economizer. At the same time, a pipe is connected to the water tank at the outlet of the economizer. This pipe is called a recirculation pipe. When the boiler is started, the water in it circulates continuously with the water tank.
Arrangement of the economizer serpentine pipe in the tail shaft.
For low-quality fuels with high ash content, the economizer heating surface design should adopt appropriate anti-wear measures to effectively solve the wear problem. In addition to using large-diameter thick-walled pipes and tube bundles for sequential arrangement in the economizer heating surface design, various forms of anti-wear devices are mainly installed for parts that are prone to wear.
In recent years, in order to further enhance heat transfer, finned tube economizers and membrane economizers have been used and have achieved certain results.
The cost of finned tubes is slightly higher, while the cost of welding 2-3mm thick flat steel in the middle is slightly cheaper.
Both finned tube economizers and membrane economizers can increase the heating area on the flue gas side by about 30%, thereby reducing the metal consumption per unit evaporation, and reducing resistance and ash accumulation.
 dtfinnedtube.com
dtfinnedtube.com