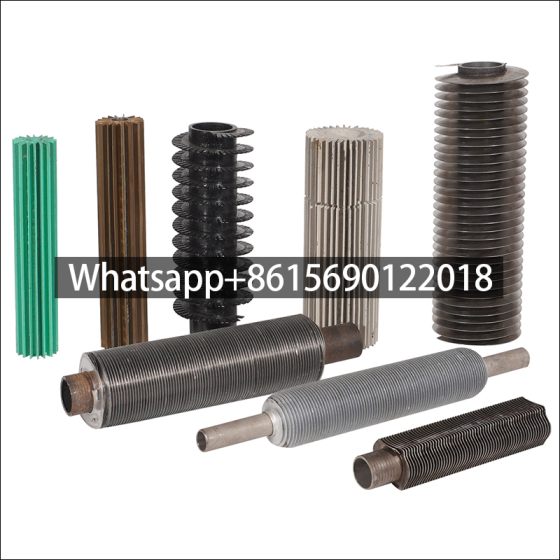
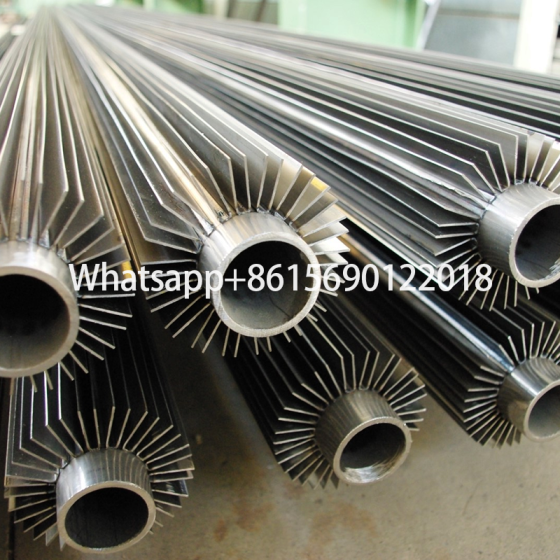
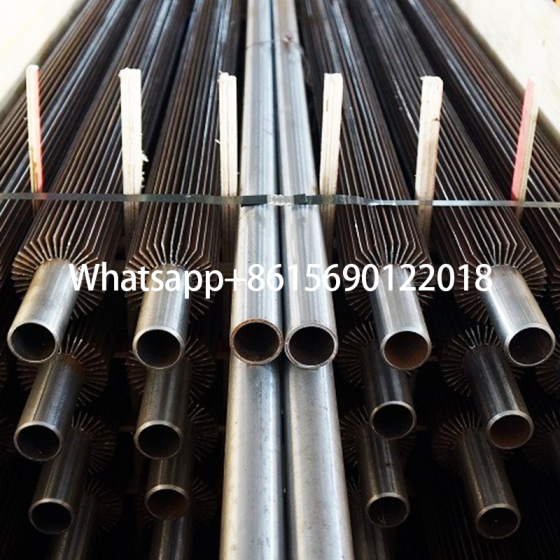
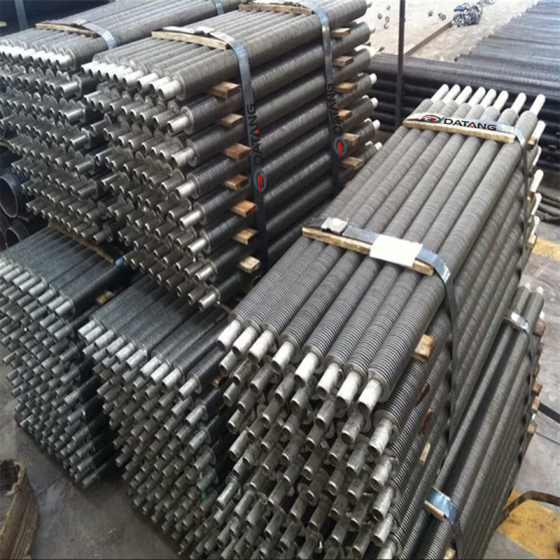
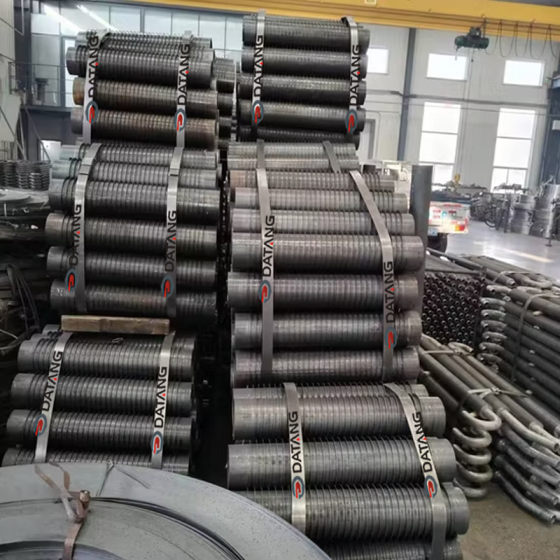
What are longitudinal finned tubes?
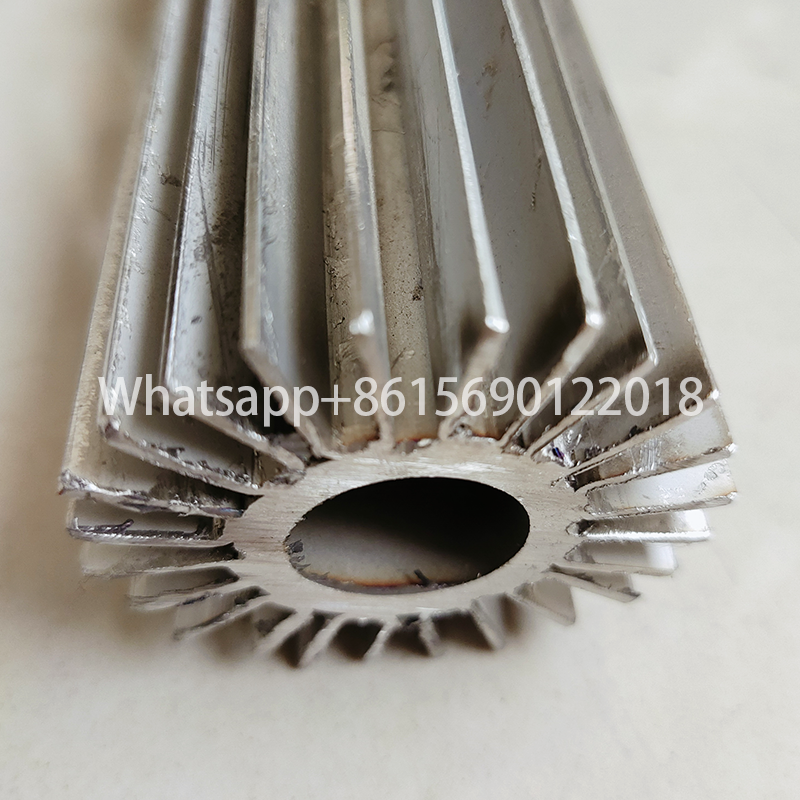
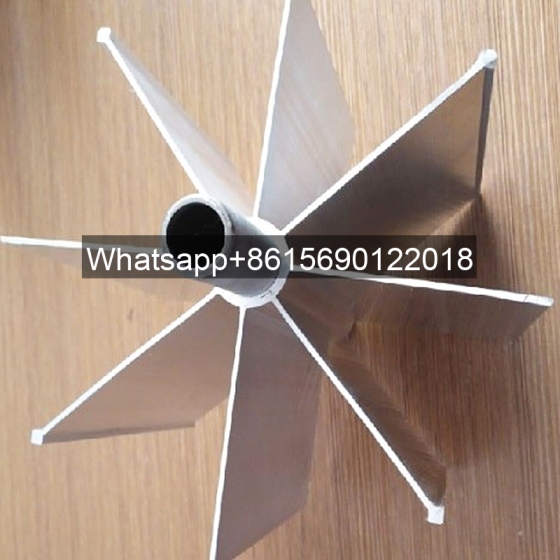
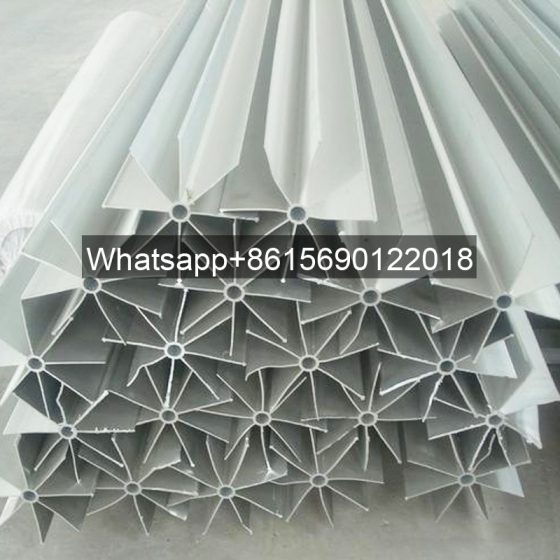
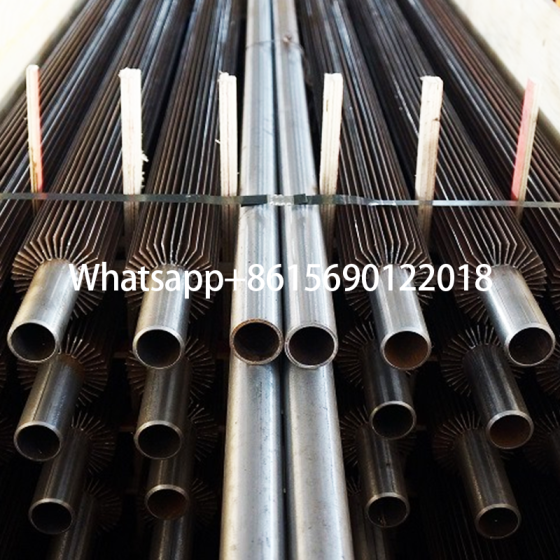
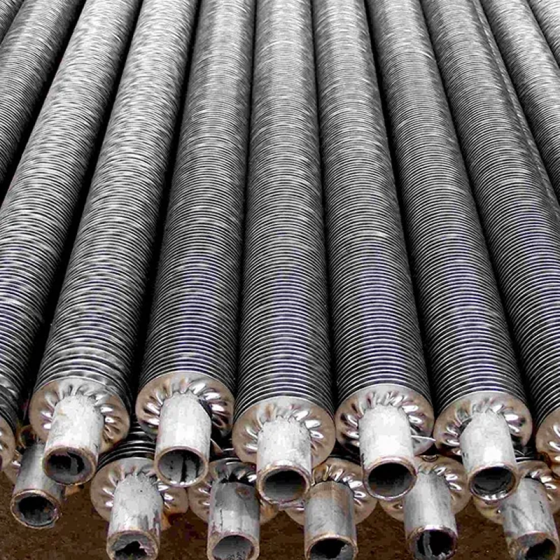
Longitudinal finned tubes for heat exchangers are components that enhance heat exchange efficiency by welding longitudinal fins on the base tube. They are mainly used to improve heat exchange performance in high temperature, high pressure and corrosive environments.
Structural characteristics of longitudinal finned tubes
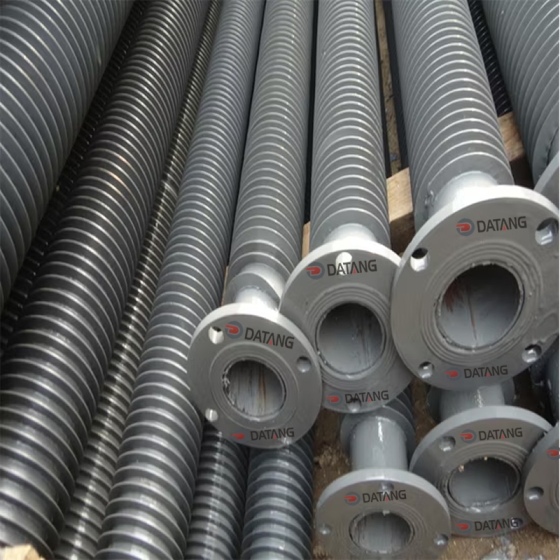
The fin direction of the longitudinal finned tube is consistent with the direction of the heat exchange tube, and more efficient heat transfer is achieved by increasing the surface area. This structure is mostly used in shell and tube heat exchangers, especially in petrochemicals, industrial boilers and other scenarios.
Manufacturing process of longitudinal finned tubes
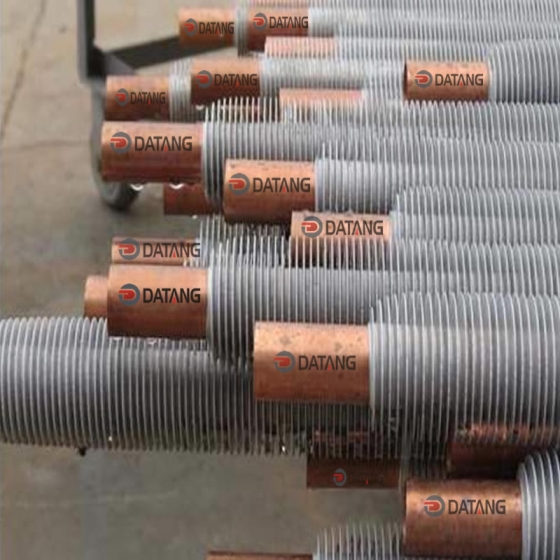
Common manufacturing methods include high-frequency welding and mechanical winding. The high-frequency welding process can make the fins and the base tube more tightly combined, with higher heat transfer efficiency and strong adaptability.
Application scenarios of longitudinal finned tubes
Applicable to steam environments, waste heat recovery devices and air conditioning heat exchangers, etc., and can adapt to complex working conditions while ensuring efficient heat dissipation.
Longitudinal finned tubes are key components used in heat exchangers to enhance heat transfer. They increase heat transfer efficiency by increasing surface area and are widely used in high temperature, high pressure and corrosive environments in the industrial field. Its core advantages include corrosion resistance and wear resistance, and are suitable for waste heat recovery and heat exchange equipment.
It is mainly used in heat exchangers in industrial fields such as petrochemicals, electricity, and metallurgy, such as heat pipe heat exchangers and waste heat recovery equipment. In the waste heat recovery scenario of ash-rich flue gas, longitudinal finned tubes can significantly improve heat transfer performance and reduce flow resistance.
Advantages of longitudinal finned tubes
Compared with circular finned heat exchangers, longitudinal finned tubes have lower metal consumption and smaller flow resistance under the same heat recovery conditions. Experimental data show that its heat transfer performance is slightly better than that of circular finned heat exchangers, especially when dealing with ash-rich flue gas, it is more stable.
 dtfinnedtube.com
dtfinnedtube.com