Serrated Fin Tubes: Structure, Advantages, and Applications
Introduction
Serrated fin tubes are advanced heat exchange components widely used in industrial and commercial systems due to their exceptional thermal efficiency and durability. This article explores their material composition, specifications, key features, advantages, packaging standards, and real-world application cases.
1. Serrated Fin Tube Material Composition
Serrated fin tubes are typically constructed from dual materials to balance strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal performance:
- Base Tube Materials: Carbon steel (ASTM A179/A192), stainless steel (304/316L), or alloy steel (e.g., Incoloy 800) for high-temperature and corrosive environments.
- Fin Materials: Aluminum, copper, or stainless steel fins welded to the base tube. Bimetallic designs (e.g., aluminum fins on a carbon steel tube) are common to enhance corrosion resistance and reduce costs.
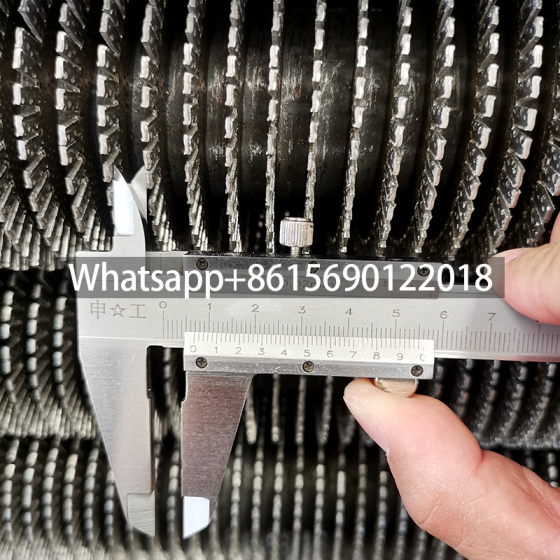
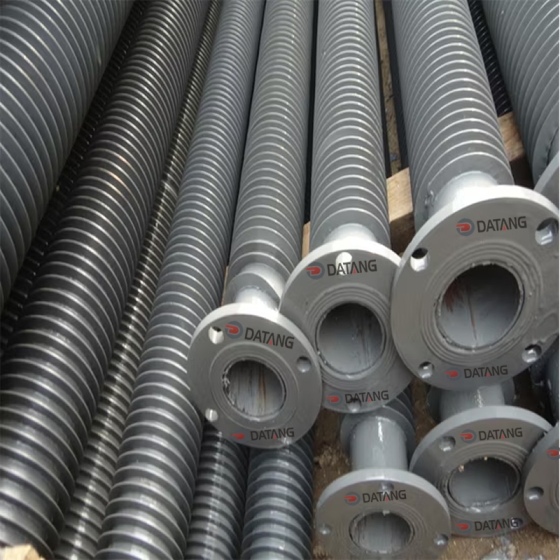
2.Serrated Fin Tube Specifications
Standard specifications vary based on application requirements:
- Outer Diameter: 15–50 mm (base tube), with fin heights of 8–20 mm.
- Fin Density: 80–300 fins per meter, with serration depth of 0.5–2 mm.
- Length: Up to 12 meters for seamless installation, minimizing joints.
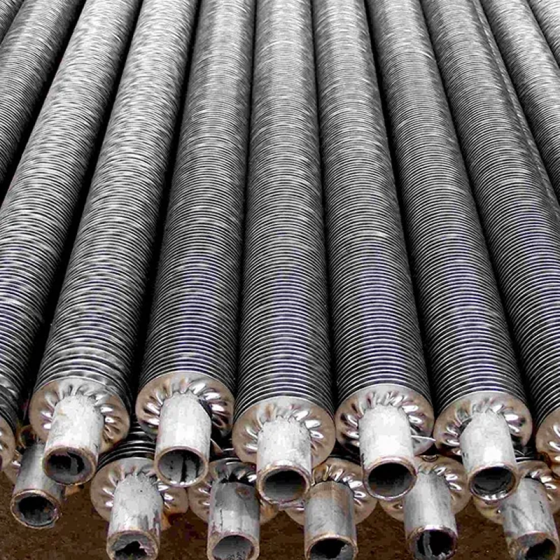
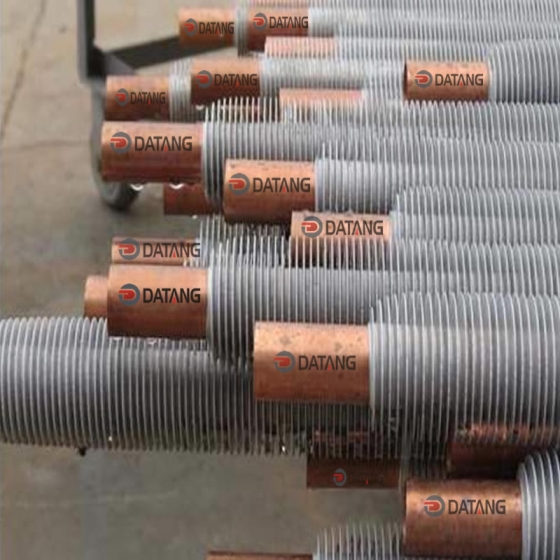
3.Serrated Fin Tube Key Features
- Serrated Fin Design: Precision-cut teeth on fins disrupt laminar flow, inducing turbulence and enhancing heat transfer efficiency by 30–50% compared to smooth tubes.
- Robust Welding: High-frequency welding ensures a metallurgical bond between the fin and base tube, suitable for high-pressure (≤30 MPa) and high-temperature (≤600°C) operations.
- Corrosion Resistance: Optional coatings (e.g., galvanization) or material combinations extend service life in harsh environments.
4.Serrated Fin Tube Advantages
- Superior Heat Transfer: The serrated structure increases surface area by 5–10 times, accelerating heat exchange in gas-to-liquid or liquid-to-liquid systems.
- Energy Efficiency: Reduces energy consumption by 20–30% in HVAC and industrial processes, supporting sustainability goals.
- Low Maintenance: Resists fouling and corrosion, minimizing downtime in chemical or power plants.
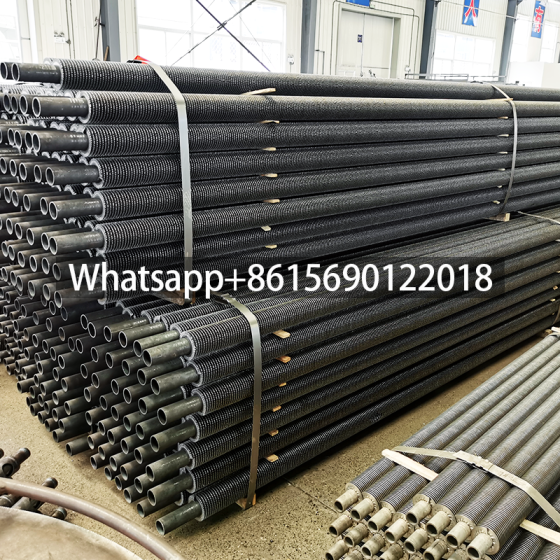
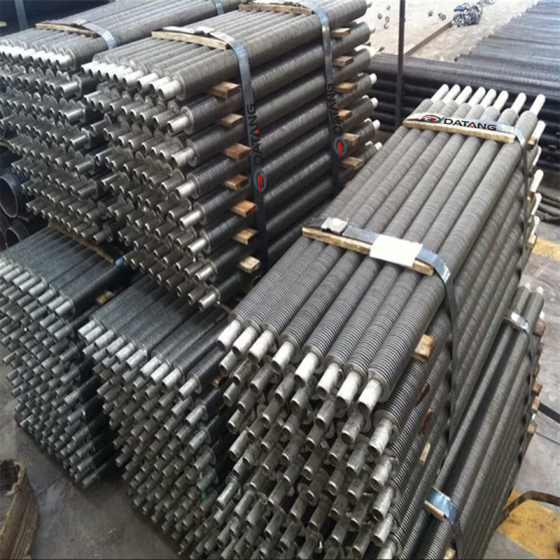
5.Serrated Fin Tube Packaging Standards
To ensure safe transportation and storage:
- Protective Coating: Anti-rust oil or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper is applied.
- Bundling: Tubes are grouped in wooden crates or steel frames with foam spacers to prevent abrasion.
- Marking: Each package includes material grade, dimensions, and QR codes for traceability.
6.Serrated Finned Tube Application Cases
Case 1: Petrochemical Industry
- Application: Heat recovery in refinery gas coolers.
- Specifications: Stainless steel (316L) tubes with aluminum fins.
- Result: Improved heat recovery efficiency by 40%, reducing fuel costs.
Case 2: Power Plant Boilers
- Application: Flue gas waste heat utilization.
- Specifications: Carbon steel base tubes with galvanized steel fins.
- Result: Extended equipment lifespan by 15% in high-sulfur gas environments.
Case 3: Food Drying Systems
- Application: Hot-air drying for grain processing.
- Specifications: Copper-nickel alloy tubes for hygienic heat exchange.
- Result: Achieved uniform drying with 25% faster processing times.
Conclusion
Serrated fin tubes are indispensable in modern thermal systems, offering unmatched efficiency, adaptability, and reliability. Advances in materials and manufacturing continue to expand their use in renewable energy, waste heat recovery, and smart HVAC systems, reinforcing their role in sustainable industrial development.
 dtfinnedtube.com
dtfinnedtube.com